FLEMISH ART
Following the settlement of the Madeira archipelago, Prince Henry promoted the introduction and cultivation of sugarcane in 1425. The successful adaptation of the species and the massive production and export of sugar throughout Europe , dictated the development of a prosperous commercial cycle.
The growing needs of local communities, including devotional ones, stimulated commercial exchanges. From the cities of Bruges, Louvain, Brussels and Antwerp, in the Flanders region, where Madeira's sugar was sold, works of art were imported – paintings, sculptures, liturgical implements, vestments and funerary plaques.
The growing needs of local communities, including devotional ones, stimulated commercial exchanges. From the cities of Bruges, Louvain, Brussels and Antwerp, in the Flanders region, where Madeira's sugar was sold, works of art were imported – paintings, sculptures, liturgical implements, vestments and funerary plaques.
Painting
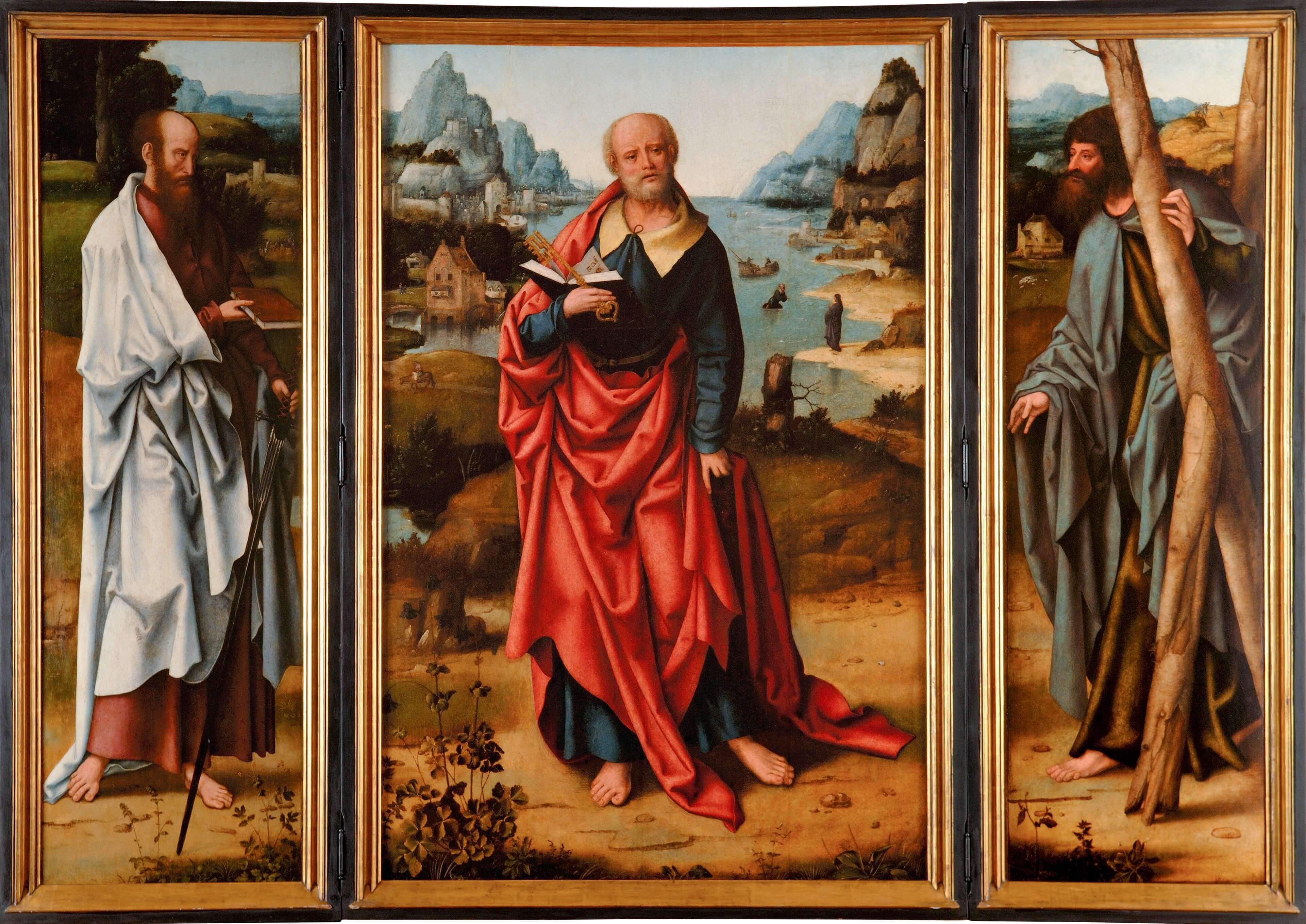

Triptych of Saint Peter, Saint Paul and Saint Andrew
Attributed to Joos Van Cleve and his collaborators
Flanders, Antwerp
Flanders, Antwerp
<> 1520
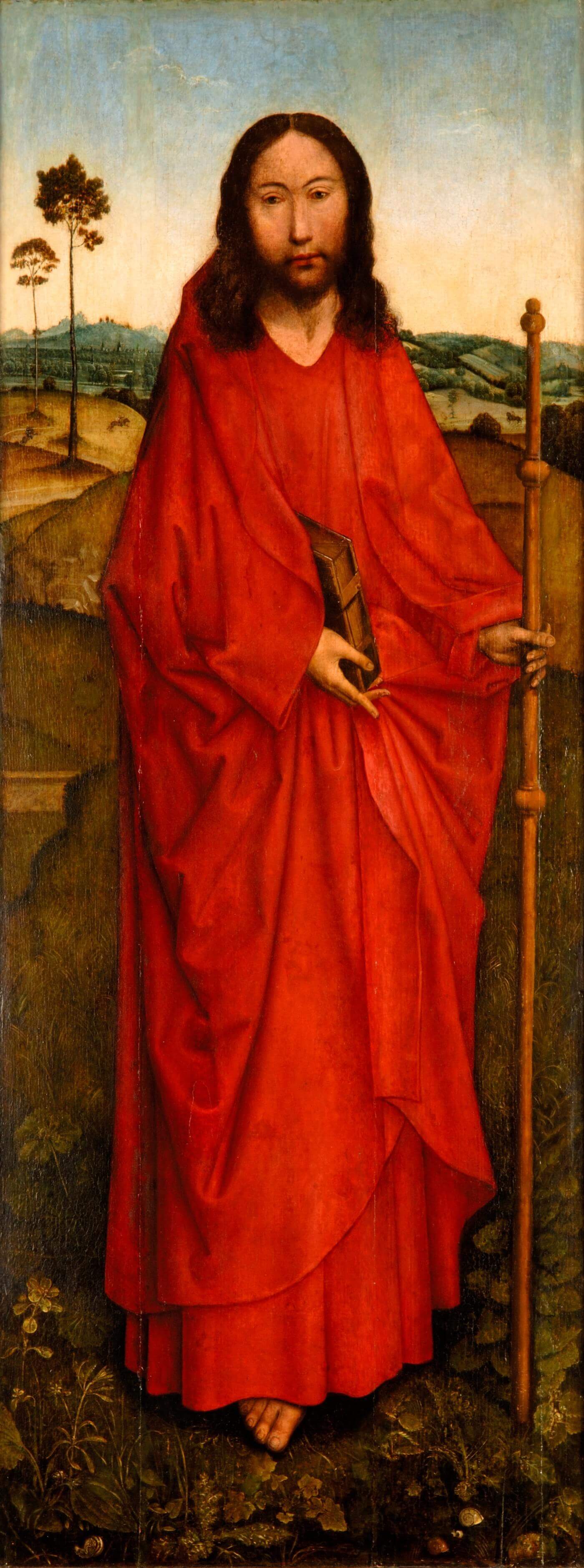

Saint James
Attributed to Dierc Bouts
Flanders, Bruges
Flanders, Bruges
1451 <> 1500
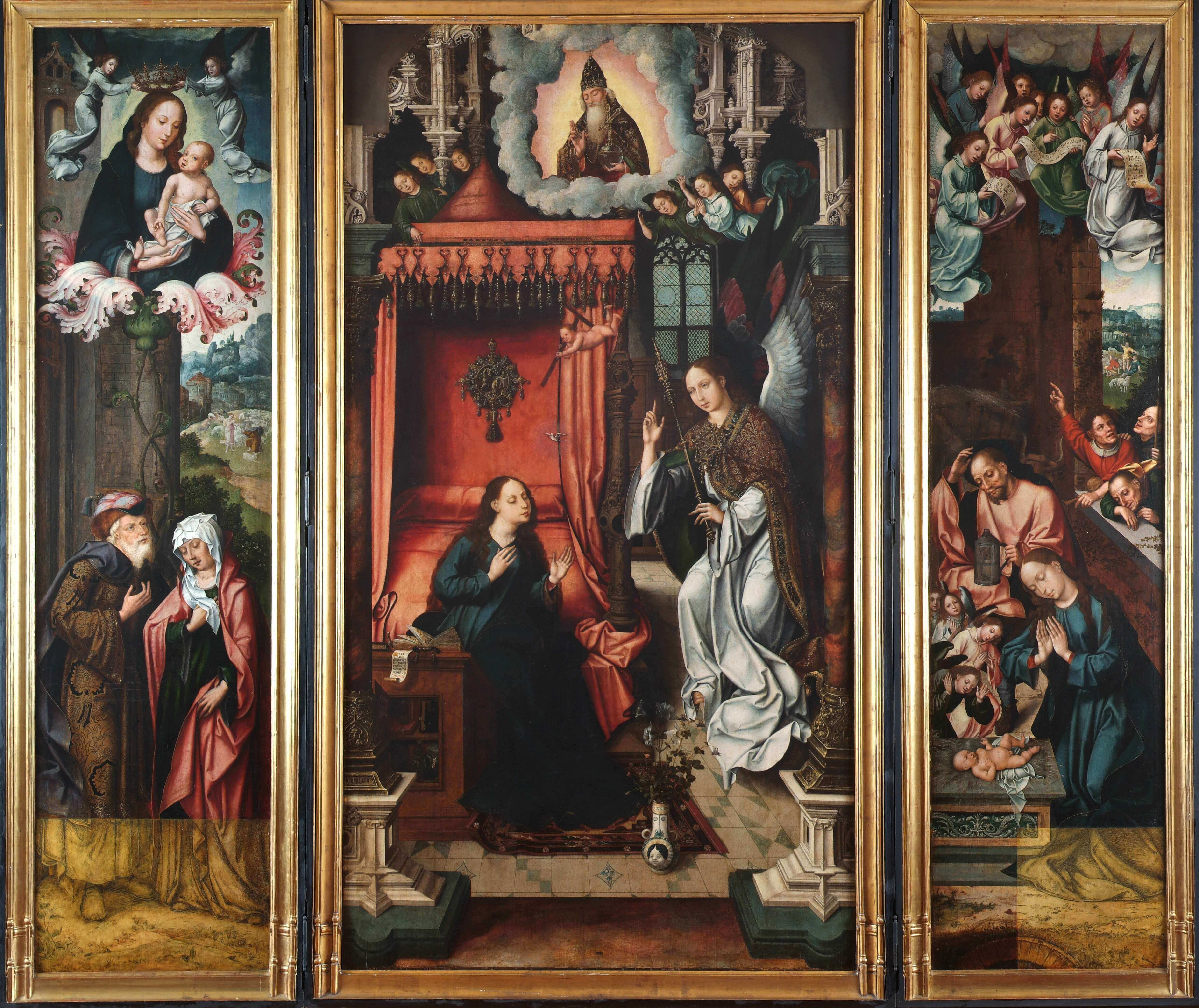

Triptych of the Incarnation
Attributed to Joos Van Cleve and his collaborators
Flanders, Antwerp
Flanders, Antwerp
1510 <> 1515

Wings of the Triptych of Mother Church of Calheta
Attributed to Jan Provoost
Flanders, Antwerp
Flanders, Antwerp
1525 <> 1529
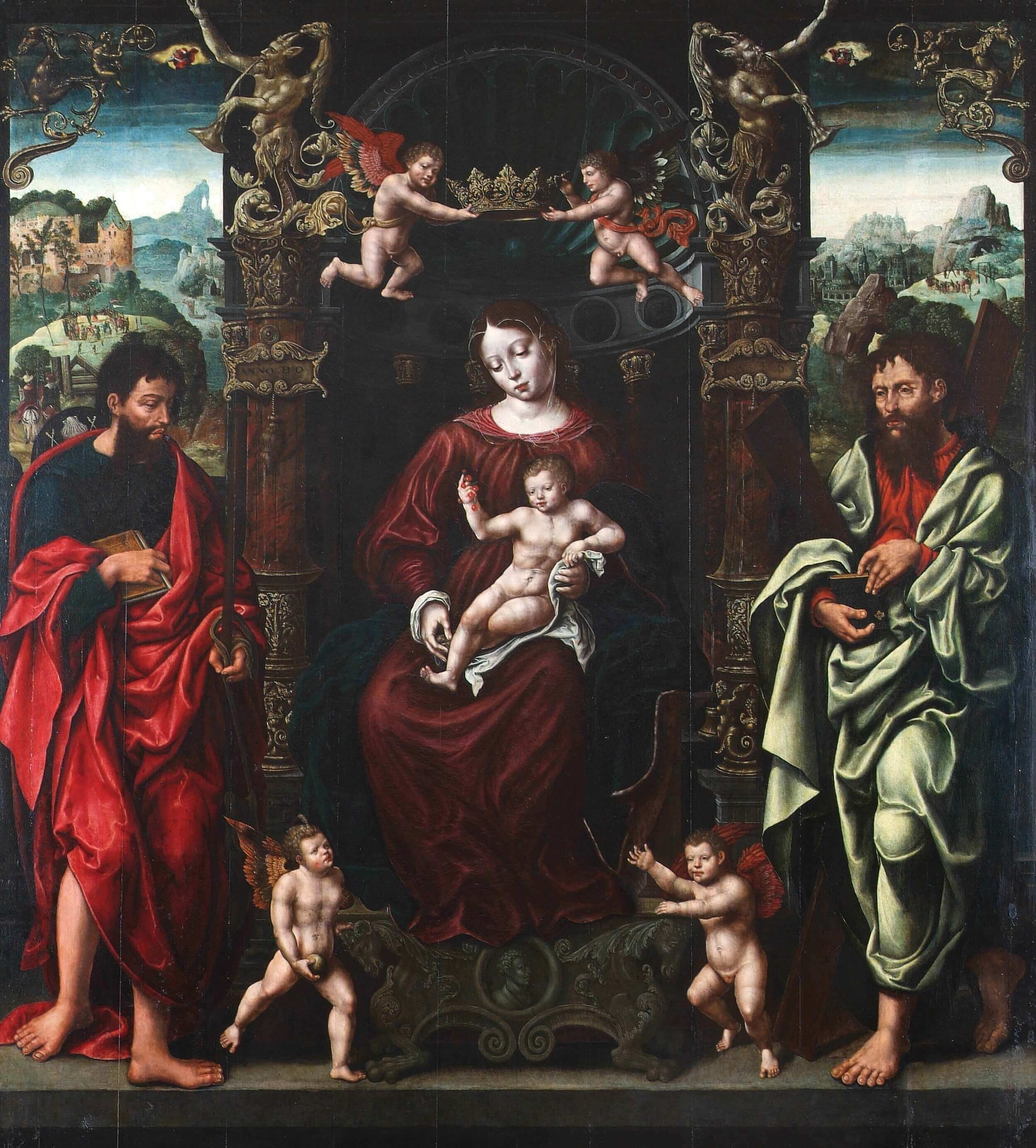

Virgin of “Amparo”
Attributed to Jan Gossart named Mabuse and his followers
Flanders, Antwerp
Flanders, Antwerp
1543
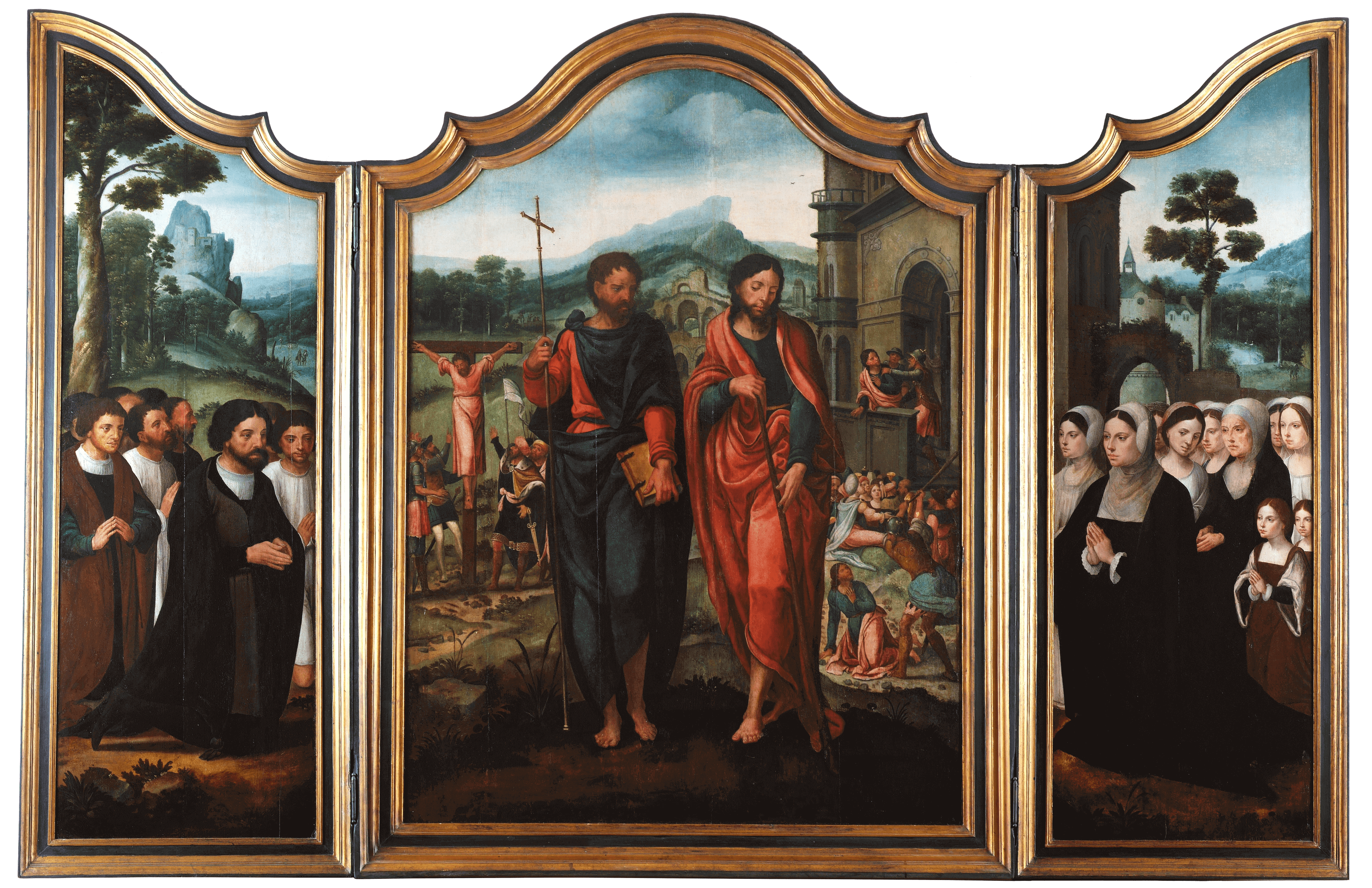
Triptych of Saint James the Minor and Saint Philip
Attributed to Pieter Coeck Van Aelst
Flanders, Antwerp
Flanders, Antwerp
1527 <> 1531
Sculpture
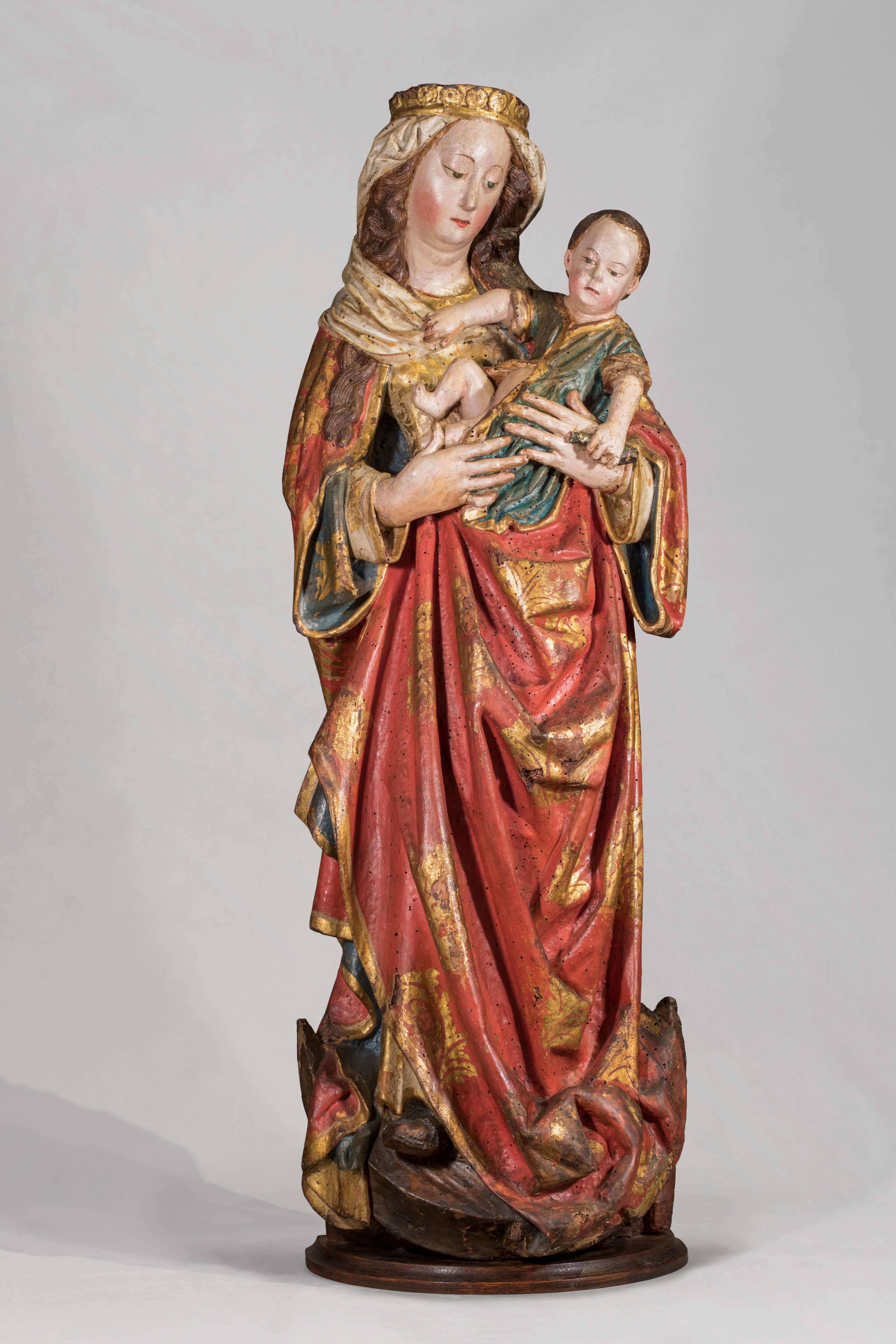

Immaculate Conception of Mary
Flanders, eclectic workshop from Mechelen-Brussels hub
1501 <> 1510
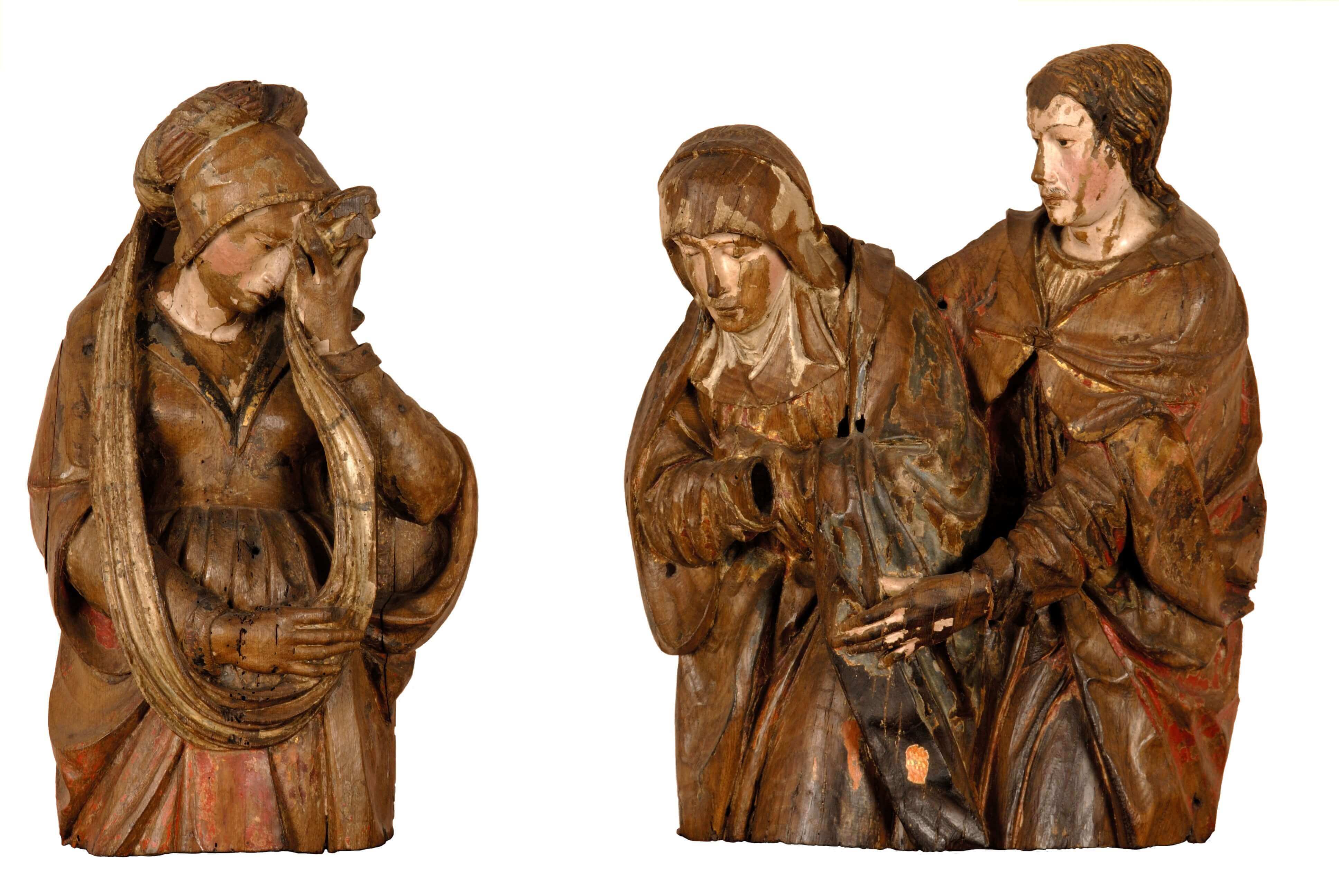

Figures of a deposition of Christ in the tomb: Mary of Clopas, Virgin Mary and Saint John
Flanders, Mechelen
1501 <> 1510
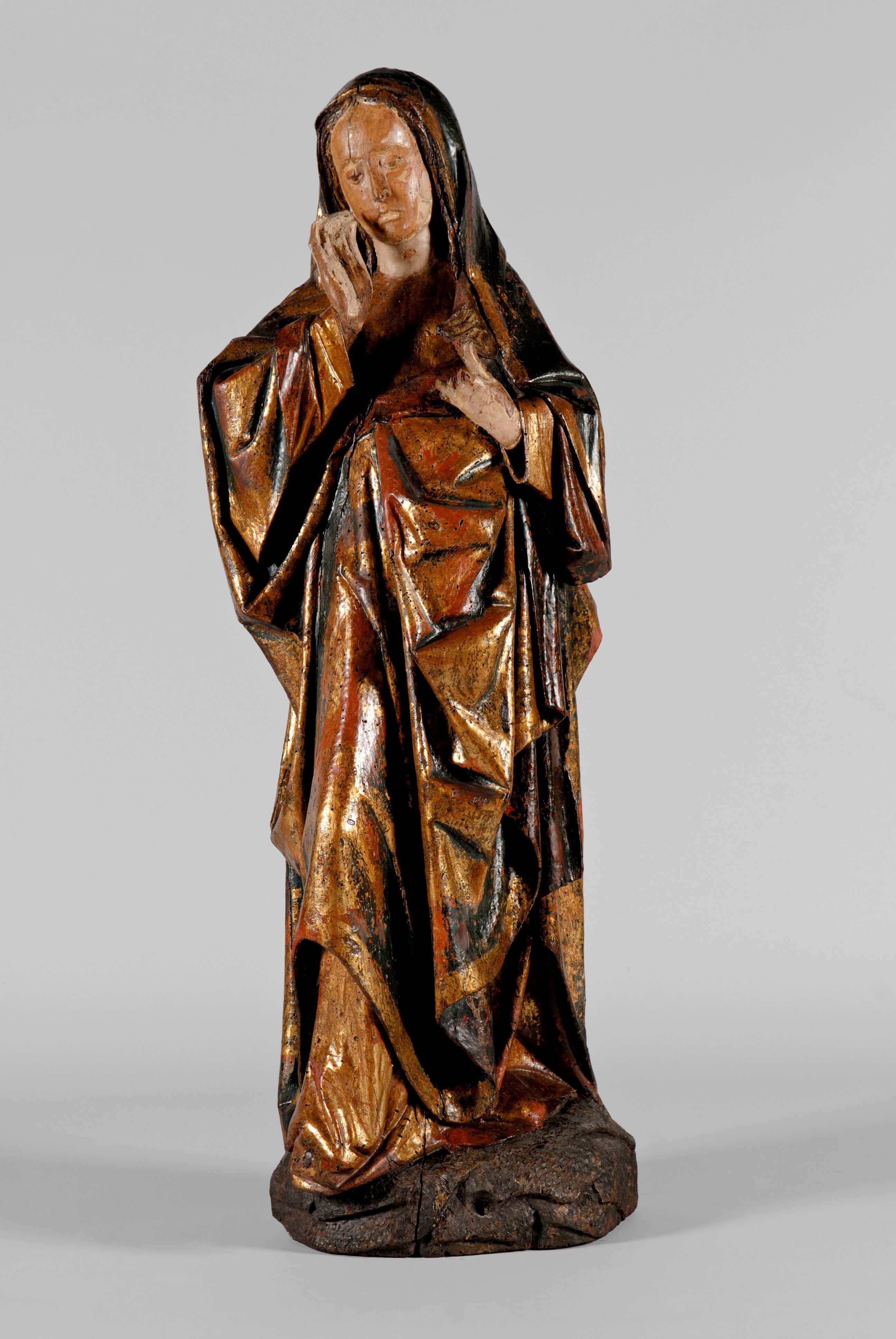

Figures of a Calvary: Mother of Sorrows
Attributed to Fernão Muñoz (Hispano-Flemish artist)
Portugal
Portugal
1501 <> 1525
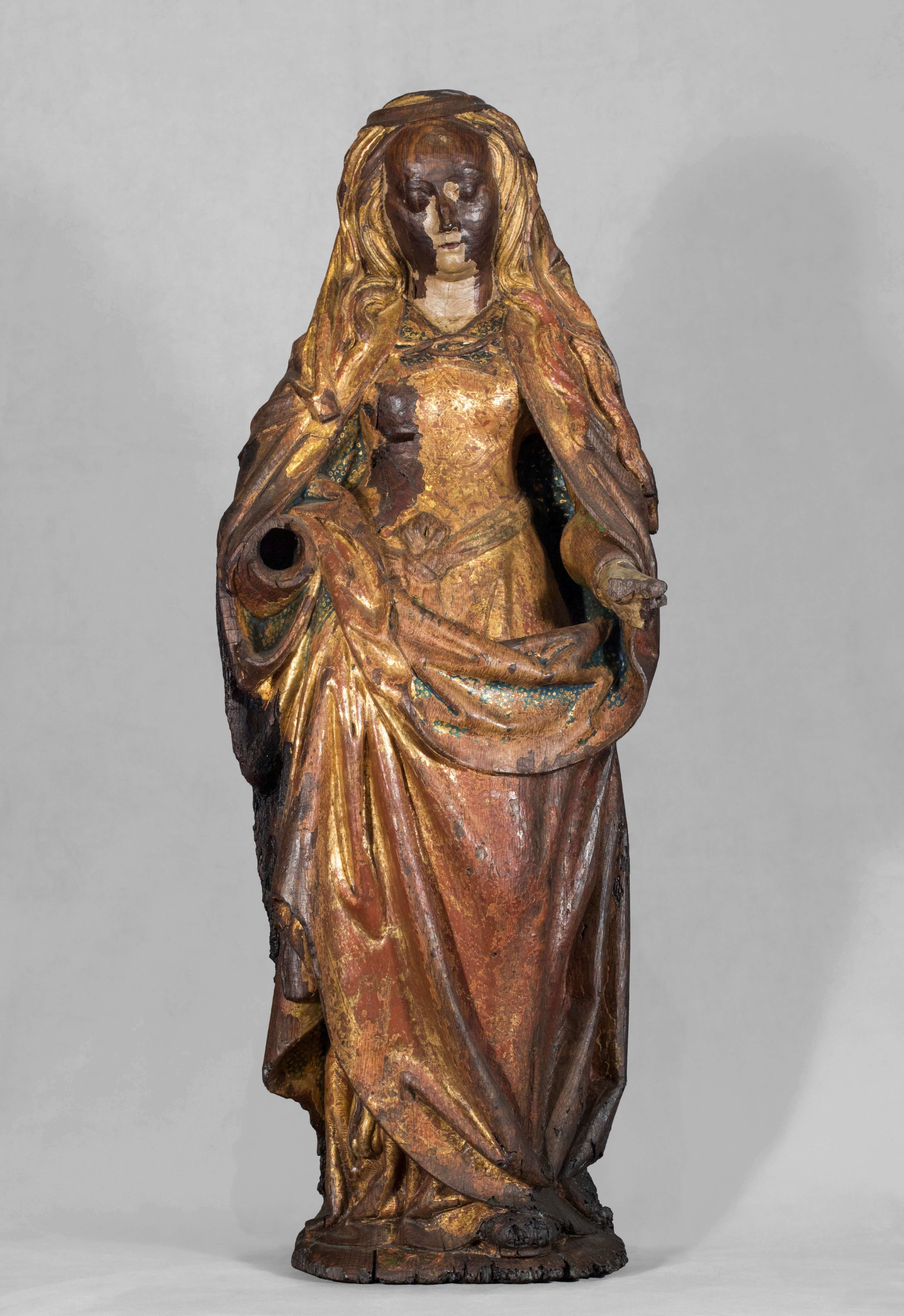

Saint Lucia
Flanders, Mechelen
1501 <> 1510
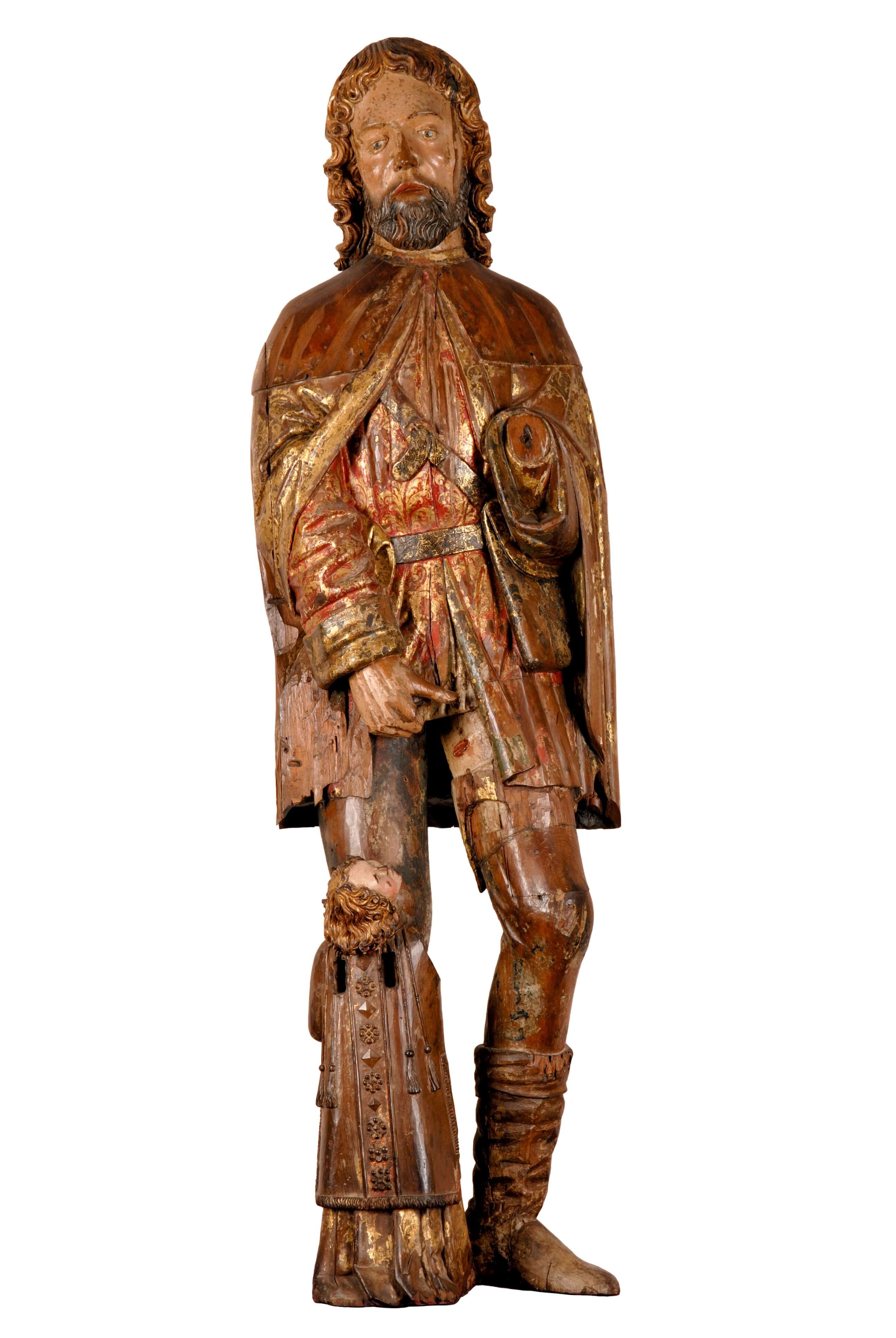

Saint Roch
Flanders, Mechelen
1521 <> 1525
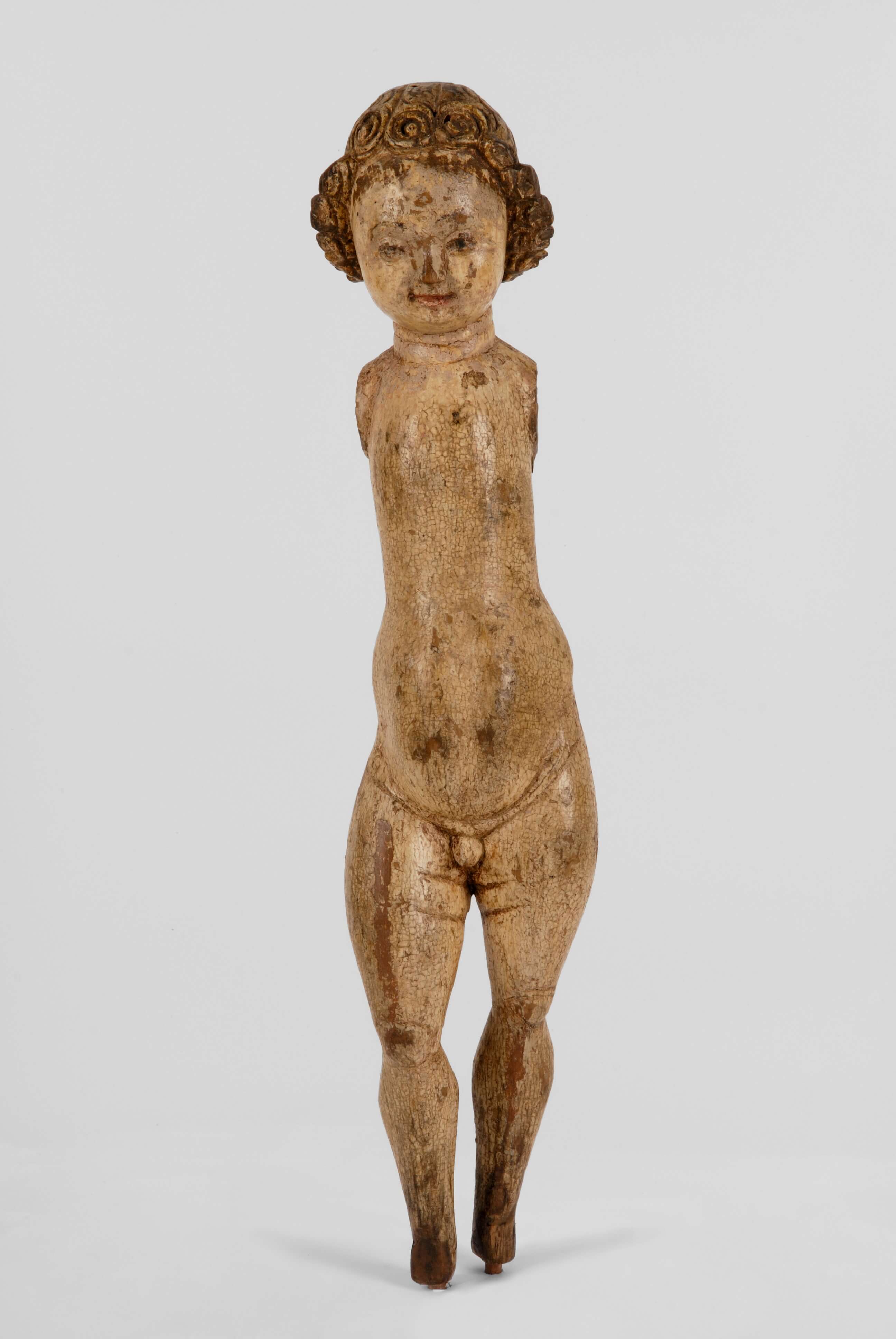

Infant Jesus
Flanders, Mechelen
1501 <> 1510




